Bosch-Rexroth Roller vs. Ball rail guides

Bosch-Rexroth roller rail guides, which utilize cylindrical or barrel-shaped rollers rather than circular balls for the load–bearing components, are ordinarily correlated to machine tool applications. However, the performance benefits that rollers bring to machining centers can be beneficial in different applications, too. If you’re planning a machine or system that requires linear movement, consider these three advantages that roller rail guides offer compared to Bosch-Rexroth ball rail guides.
Sectional view of roller rail guide Bosch-Rexroth
| See prices, stocks and CAD in the online store! |
Online store |
1. Load capacity
When exposed to a load, rollers create line contact with the guide surface, which is a lot bigger than the point contact that is created when balls are exposed to a load. This gives roller rail guides higher load capacities than ball rail guides of the same size.
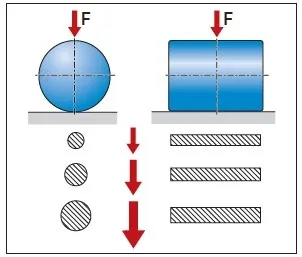
Balls under load create point contact with the raceway, while rollers under load create line contact.
This higher load capacity of Bosch-Rexroth roller guides is additionally enhanced by the bearing life equation for rollers. Instead of being exponentiated to 3, likewise with ball rail guides, the life equation for roller rail guides is exponentiated to 10/3, which implies that even a little benefit in load capacity for a roller bearing versus a ball bearing means a much higher travel life for the roller version.
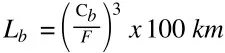
Ball Rail Guide Life Equation
(C=load capacity; F=force)
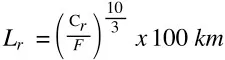
Roller Rail Guide Life Equation
(C=load capacity; F=force)
For instance, a size 25 Bosch-Rexroth ball rail guide with a load capacity of 20,000 N and an applied force of 2000 N, will have a dynamic travel life of 100,000 km. A same-size Bosch-Rexroth roller rail guide, with 24,000 N load capacity and 2000 N applied force will have a dynamic travel life of 395,600 km!

A ball rail guide with a load capacity of 20,000 N and applied force of 2000 N has a travel life of 100,000 km.
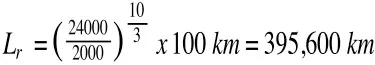
A roller rail guide of the same size, with load capacity of 24,000 N and applied force of 2000 N has a service life of 395,600 km.
In applications where ball rail guides would fail to provide adequate travel life, or where the necessary size would be too extensive to be practical, roller rail guides can give a solution.
Product Manager for Linear Motion and Machine Tool Products at Bosch-Rexroth, gives the case of an infusion molding company that needed to implement mechanized part loading and unloading, but the machine’s plan didn’t permit access for the loading/unloading gear. The solution was to extract the four linear shafts that upheld the panel at its corners and change them with roller rail guides that hold the panel from the base. This opened up the top space so the part loader/unloader could get to the machine. For this situation, Bosch-Rexroth roller rail guides were the main arrangement that could give the load capacity and travel life that the client required, because of the extremely high moment loads.
| Send Inquiry! | info@tuli.si |
2. Capacity to downsize
As the example above shows, the higher load capacity and longer travel life of roller linear guides imply that planners can frequently utilize roller guides that are one or two sizes smaller (for instance, size 25 instead of size 45) than the ball linear guides that would be expected to accomplish same travel life.
This downsizing of the Bosch-Rexroth linear guides can be particularly advantageous in multi-axis or gantry applications, where weight saved on one axis has a trickle-down effect on the supporting axes, possibly saving tens of thousands of euros in constituent costs.
In a three-axis Cartesian or gantry crane system, diminishing the mass of the Z axis decreases the static and dynamic forces on the Y axis, which implies that the Y axis can possibly be downsized. Likewise with the X axis – by decreasing the mass of the Y and Z axes, it may be conceivable to downsize the X axis, since the forces performing on it are diminished. What's more, this downsizing applies not exclusively to the linear guides, but also to the other drive componenets (linear engine, ball screw, etc.), engine, and other parts, such as couplings, gearboxes, and cable carriers. This gives savings in material cost, energy usage, and space.
3. Higher rigidity
The line contact created by rollers also gives higher rigidity than the point contact created by balls, which is the essential explanation why roller rail guides are so widely utilized in machine devices. In any case, application engineer at Bosch Rexroth, mentions that printing processes that include pressing, for example, flexographic printing and narrow web printing, also have advantages from the rigidity of roller rail guides. Less deflection of the guide block means less deflection of the printing head, which results in a higher quality print.
We can see clients in the woodworking industry who utilize roller rail guides for their higher rigidity, particularly in processes with high shock loads, for example veneering. Bosch Rexroth engineer also mentions that sealing is even more important for roller rail guides than for ball rail guides. This is because in a ball rail guide, the balls can push residues to an area outside the contact zone, since the balls only have point contact with the raceway. But the line contact that rollers create with the raceway leaves no place for the remains to go that will be outside the load zone, so any amount of remains that advances into the carriage will affect life and performance.
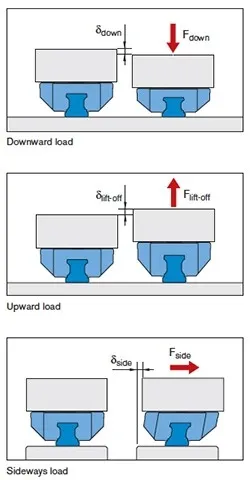
Deflection can be caused by downward, upward, or sideways forces.
When contrasting ball and roller rail guides from Bosch-Rexroth, planners will find that roller rails are more costly than ball rails. But as Bosch-Rexroth engineer mentions, the best measurement for contrasting expense is not the price of the parts, but the expense per km of travel. In the example above, if the ball linear guide costs 1000 EUR and has a travel life of 100,000 km, its expense per km of travel is 0.01 EUR. If the roller linear guide costs 25 percent more, at 1250 EUR, but has a travel life of 395,600 km, its expense per km of travel is just 0.003 EUR (less than half a cent).
If your application needs very high load capacities or considerable rigidity, or if you’re planning a large gantry where weight and space investment are crucial, compare the performance and expense of Bosch-Rexroth roller rail guides with that of ball rail guides. You may be amazed to find out that roller rails give a better complete expense of ownership in your application.




























Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *