MINIATURE PROFILED RAILS

For their size profiled rails have a high load-carrying capacity. Yet when precise fluid motion is required and the loads being moved are not high, they can be classified as overkill for the application in question. This is the reason that most profiled linear rail guide manufacturers now make miniature iterations, with similar performance benefits and characteristics of conventional sized profiled rails, but with a smaller form factor.
Although there is no official classification for miniature profiled rails, most manufacturers label linear rail guide sizes 15 and smaller as miniature, with existing sizes as small as one millimeter in rail width.
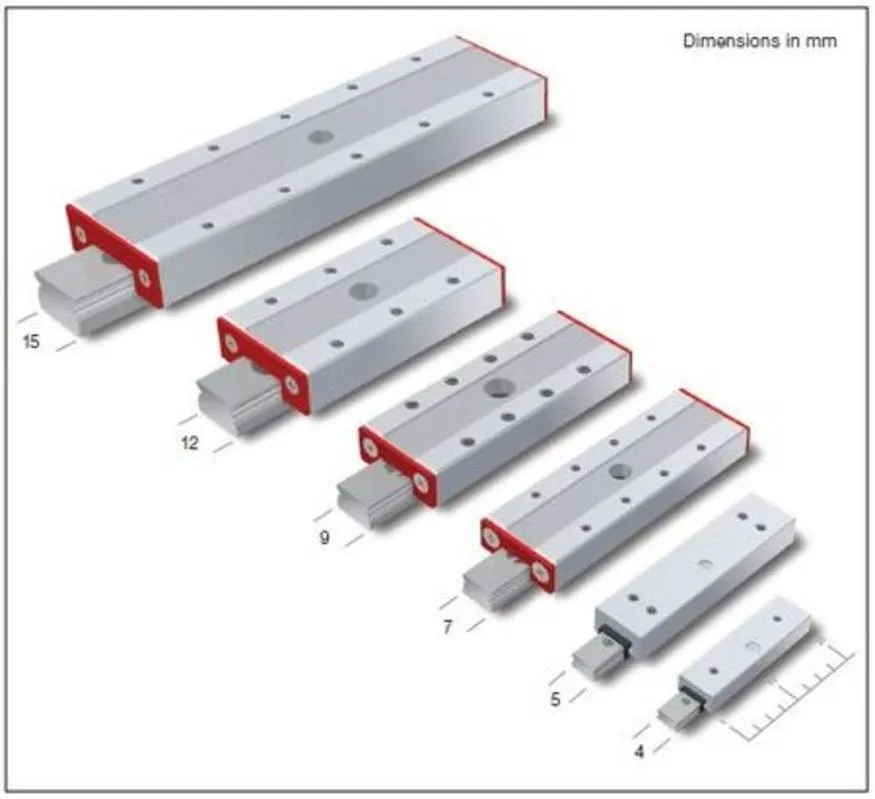
MINIATURE RAILS VS STANDARD ONES
Small form factor aside, the other most notable difference between standard and miniature linear profiled rails is the number of rows of circulating balls in the bearing. Standard sized bearings tend to have 4 rows of balls (two on each side), which is the reason for their high load and moment capacity. Due to their compact sizes, miniature rail guides usually have only 2 rows of circulating balls (one on each side). Unfortunately, this reduces their load as well as moment capacities. Also, it is to be noted that longer versions of miniature rails provide an increase in pitch and moment capacity, while wider versions have a greater roll moment capacity.
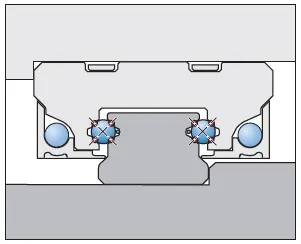
Another key distinction between miniature and standard profiled rail guide bearings is the ball retention in the bearing housing. The importance of this is paramount since all standard sized rails have the balls retained in the housing, which prevents the balls from falling out during installation and general handling. Because of their limited size, miniature guide rails generally do not include ball retention mechanisms, but if they do, they are effective only when handled with care. Due to the challenges with ball retention, miniature profiled guide rail bearings are normally mounted on an arbor (basically a plastic placement holder) during the manufacturer's assembly and packaging. The plastic arbor does not just retain the balls in the bearing housing but it also helps with mounting the bearing on the rail.
TECHNICAL FEATURES
Due to their small form factor, miniature guide rails cannot be intensely preloaded, but light preloads can be achieved somewhere in the range of 1% to 2%. Accuracy grades for miniature guide rails are the same as for standard profiled guide rails, ranging from normal accuracy to super precision.
Miniature profiled guide rails tend to be used in electronics, medical industries, and semiconductors, where contamination is unlikely to happen, and more emphasis is placed on preventing contaminants from spreading into the environment by moving parts. Miniature guide rails meet this requirement with the help of low-friction or non-contact seals. Conversely, a lot of manufacturers offer secondary seals for instances where the bearing require extra protection against contaminants. As for applications within corrosive environments, miniature guide rails are regularly supplied with parts made of corrosion-resistant or stainless steel.
To advance their support for applications in clean environments, manufacturers have started to submit their designs for cleanroom compatibility testing. ISO 14644-1 class 4 and 5 (US Fed Std 209E Class 10 and 100) qualifications for particle generation can be achieved, with the use of low-friction seals and cleanroom grease.
In conclusion miniature guide rails are more than just smaller iterations of standard guide rails. They offer to the table a compact solution for linear motion applications that need precise and smooth motion with minimized particle generation as well as lower load and moment-handling requirements.



























Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *