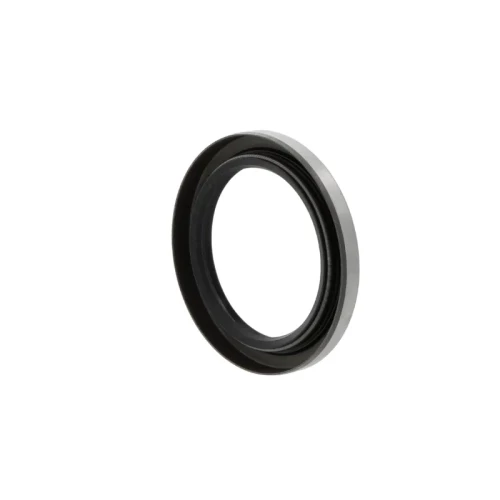
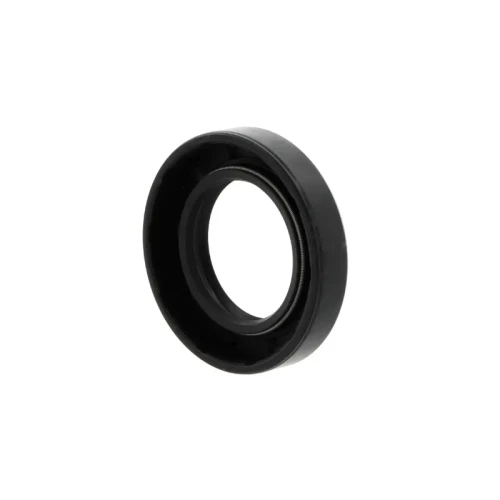
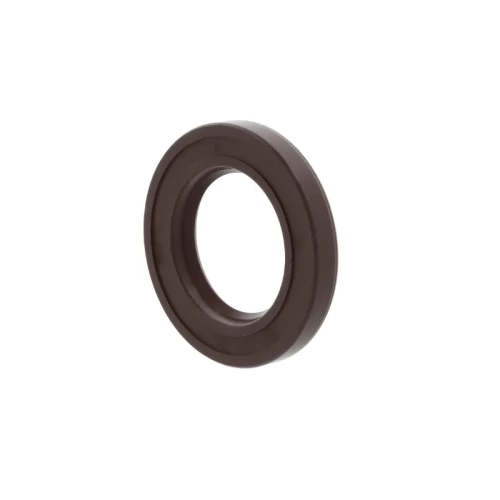
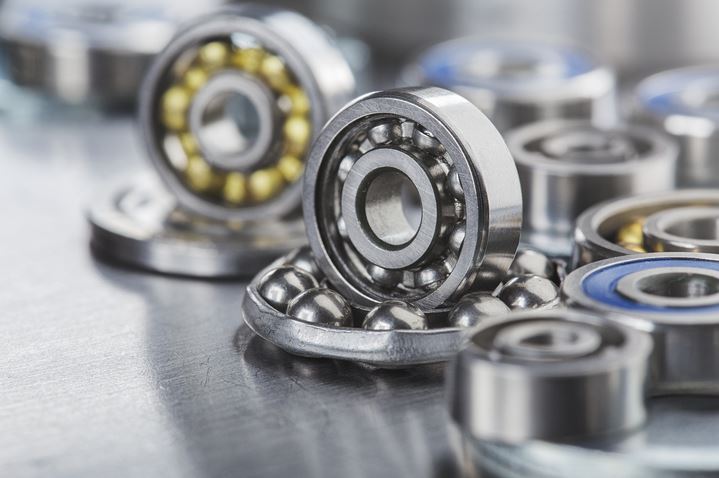
Oil seals
Oil seals play a crucial role in the safe operation of machinery since they ensure that lubricants stay in and contaminants stay out.
Moreover, when compared to some of the components they protect from damaging due to contamination, oil seals are inexpensive. Yet, they provide high value.
Bellow we'll delve into what oil seals are, the materials they are made of, their working temperature ranges, and their diverse applications.
| For ADVANCED SEARCH of oil seals go to: | Oil seals & bearings configurator |
What are Oil Seals?
Oil seals are machine components designed to prevent the leakage of lubricants such as oil or grease in rotating or moving parts of machinery.
They act as barriers, sealing the gap between stationary and moving components, ensuring the efficient performance and longevity of the equipment. A common example is found in bearings where seals are used to guarantee the grease performs well for a longer period, thus extending the lifespan of the bearing.
Materials of Oil Seals
Oil seals are fabricated from various materials to suit different operational conditions. Common materials include:
- Nitrile rubber (NBR)
- Viton
- Silicone
- Polyurethane
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
- Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM)
- Neoprene
- Fluorosilicone
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR)
- Natural rubber
From the list above, we can highlight that nitrile rubber (NBR) is widely used due to its excellent resistance to chemicals, heat, and abrasion.
Viton, another popular choice, is known for its exceptional performance in high-temperature environments and resistance to a broader range of chemicals. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the application.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) oil seals boast remarkable properties, including outstanding chemical resistance, low friction, and high-temperature stability. PTFE's non-stick nature makes it effective in preventing adhesion and promoting smooth movement in various applications. Additionally, its resilience to harsh chemicals and a wide temperature range enhances its suitability for demanding environments, making PTFE oil seals a preferred choice for industries requiring robust sealing solutions.
Working Temperature Ranges
The working temperature range of oil seals is a critical factor in their selection. Nitrile rubber seals, for instance, operate effectively within a temperature range of -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F).
Viton seals, on the other hand, can withstand higher temperatures, typically ranging from -20°C to 200°C (-4°F to 392°F).
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) oil seals typically have a broad working temperature range, often ranging from -70°C to 260°C (-94°F to 500°F). PTFE exhibits excellent thermal stability, making it suitable for applications where extreme temperatures are a consideration.
It is essential to choose the appropriate material based on the temperature conditions the oil seal will encounter in its intended application.
Applications of Oil Seals
Oil seals find applications across a wide spectrum of industries, contributing to the smooth functioning of various machinery.
In automotive systems, oil seals are used in engines, transmissions, and differentials to prevent oil leakage and maintain optimal lubrication.
In industrial machinery, they play a vital role in bearings, gearboxes, and hydraulic systems, ensuring efficient operation by keeping contaminants at bay.
Oil Seals: Final Words
It is evident that these components are indispensable in maintaining the integrity of mechanical systems.
Their versatility in material options and suitability across diverse temperature ranges make them indispensable in various applications.
Finally, the choice of oil seal material, aligned with the working temperature range, is crucial for optimal performance, so make sure you are selecting correctly.
Knowledge Base
-
Read more
Aluminum extrusion brackets are mechanical components that offer great versatility and functionality in various applications. They are essential for c...
-
Read more
Linear rail brakes, also known as clamping brakes or clamping braking elements, play a vital role in achieving safe and precise positioning. Linear ra...
-
Read more
Bearing suppliers play a crucial role in various industries, offering these essential components for machinery. In this industry, we find manufacturer...