Linear Rail Brakes
Linear rail brakes, also known as clamping brakes or clamping braking elements, play a vital role in achieving safe and precise positioning. Linear rail brakes are specialized devices designed to engage with linear guide rails. When activated, they apply a controlled clamping force, bringing the carriage (the moving component) to a precise stop or holding it securely in a specific position. By understanding their working principles, benefits, and limitations, you can effectively integrate linear rail brakes into your motion control systems, guaranteeing optimal performance and safety.
This comprehensive guide dives into the world of linear rail brakes, explaining their types, functionalities, and key considerations for implementation.
Understanding Linear Rail Brakes
Linear rail brakes, also known as clamping brakes or clamping braking elements for round shafts, are specialized devices designed to engage with linear guide rails. When activated, they apply a controlled clamping force, bringing the carriage (the moving component) to a precise stop or holding it securely in a specific position.
These brakes operate through various actuation mechanisms, including:
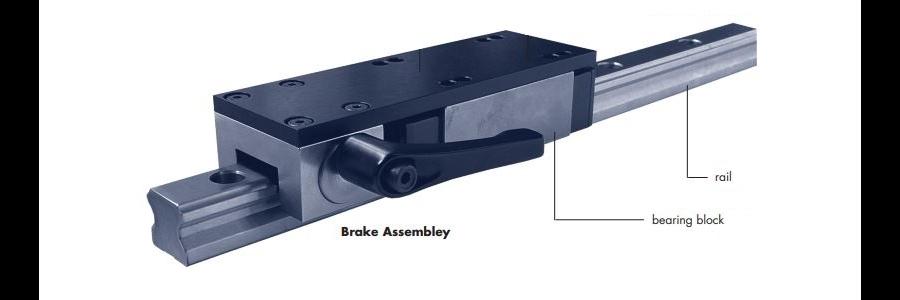
Manual: A lever or knob is used for manual engagement and disengagement. Simple and cost-effective, they're ideal for infrequent holding applications.Good examples are our ERRE.DI - FRCMAN Manual Clamp for linear guide rail and FRCCMAN Manual Clamping Element for round shaft series that come in several sizes.
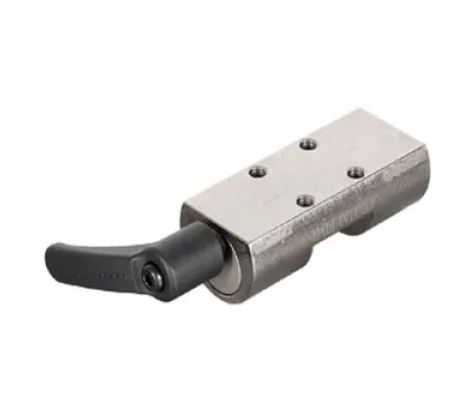

Figure 1 Manual linar rail brake
Pneumatic: Compressed air actuates a piston, which applies the clamping force. This option offers fast actuation and remote-control capabilities.
Here we find the ERRE.DI - FRC SEM Pneumatic Clamping Elements for linear guide rail and FRCC Pneumatic Clamping Elements for round shafts series.
Other options include hydraulic brakes where hydraulic fluid actuates a piston to provide high clamping force for heavy-duty applications, and electromagnetic brakes where an electromagnet engages the clamping mechanism.
Figure 2 Pneumatic linear brake for round shaft
Key Benefits of Linear Rail Brakes
Linear rail brakes offer a plethora of advantages for industrial motion control:
Enhanced Precision
By precisely controlling carriage movement, linear rail brakes ensure accurate positioning and repeatability in critical operations.
Improved Safety
They provide a secure holding force, preventing unintended movement and potential accidents, especially during power outages or emergencies.
Reduced Wear and Tear
By eliminating the need for constant motor power to maintain position, these brakes minimize wear and tear on the motor and drive components, extending equipment lifespan.
Increased Efficiency
The controlled stopping and holding capabilities of linear rail brakes optimize cycle times and improve overall production efficiency.
Versatility
Available in a wide range of sizes, actuation methods, and clamping force capabilities, these brakes cater to diverse industrial applications.
Types of Linear Rail Brakes
Linear rail brakes come in various configurations to suit specific application needs. Here are the two main categories:
- Spring-engaged Brakes: These brakes utilize spring tension to apply the clamping force. They can be activated manually, by a solenoid or pneumatic actuator that overcomes the spring tension and disengages the brake. This design offers a fail-safe mechanism, as the brake automatically engages when power is lost.
- Air-engaged Brakes: Compressed air directly applies the clamping force in these brakes. They require a continuous air supply to remain engaged and offer a fast actuation response.
Applications of Linear Rail Brakes Across Industries
Linear rail brakes find application in a wide range of industries due to their ability to ensure precise positioning and secure holding of moving components. Here's a glimpse into some key sectors that heavily rely on these brakes:
Manufacturing
- Pick-and-Place Robots: Precise stopping and holding of robotic arms during part transfer or assembly.
- CNC Machines: Secure positioning of the tool head for accurate machining operations.
- Material Handling Systems: Controlled movement and secure holding of conveyor belts and carousels.
- Packaging Machinery: Precise positioning of packaging materials for accurate wrapping and sealing.
- Food and Beverage Processing: Controlled movement of food processing equipment for precise cutting, filling, and labeling.
Semiconductor Industry
- Wafer Handling Equipment: Secure positioning of wafers during delicate cleaning, etching, and deposition processes.
- Stepper Motors: Holding the motor shaft in position for precise positioning tasks.
Automotive Industry
- Welding Robots: Precise positioning and holding of welding tools for accurate and secure welds.
- Paint Shops: Controlled movement of painting robots for uniform and consistent coating application.
- Assembly Lines: Holding car components in place during assembly processes.
Medical Device Manufacturing
- Precision Assembly Equipment: Secure positioning of delicate medical components for assembly.
- Laser Cutting Machines: Precise stopping and holding of materials during laser cutting for medical devices.
Printing and Paper Industry
- Cutting and Folding Machines: Controlled movement and holding of paper during precise cutting and folding operations.
- Printing Presses: Precise positioning of printing heads for accurate ink application.
Other Applications
- Woodworking Machinery: Secure holding of wood pieces during cutting, drilling, and shaping processes.
- Solar Panel Manufacturing: Controlled movement and holding of solar panels during assembly.
- Textile Industry: Precise positioning of fabric for cutting and sewing operations.
This list is not exhaustive, and linear rail brakes continue to find application in new and innovative ways across various industries. Their versatility and contribution to precise and secure motion control make them a valuable asset in today's automated world.
Choosing the Right Linear Rail Brake
Selecting the optimal linear rail brake for your application requires careful consideration of several factors:
Load Capacity
The brake's clamping force needs to be sufficient to overcome the moving mass and any dynamic forces involved.
Duty Cycle
Consider how frequently the brake will be engaged and disengaged. Some brakes are designed for occasional holding, while others can withstand high-cycle applications.
Actuation Method
Choose an actuation method (manual, pneumatic, hydraulic, or electromagnetic) that aligns with your control system and operational requirements.
Mounting Considerations
Ensure the selected brake is compatible with your linear guide rail size and offers easy mounting options for seamless integration.
Environmental Factors
Consider the operating temperature, dust, and humidity levels in your application environment.
Linear Rail Brakes: Some final words
Linear rail brakes play a critical role in ensuring precise and secure linear motion in various industrial applications.
By understanding their types, functionalities, and selection criteria, you can leverage these powerful devices to optimize your motion control systems and achieve peak performance in your industrial processes.
For further information and assistance in choosing the perfect linear rail brake for your specific needs, don't hesitate to contact us.




























Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *