Bearing Seals
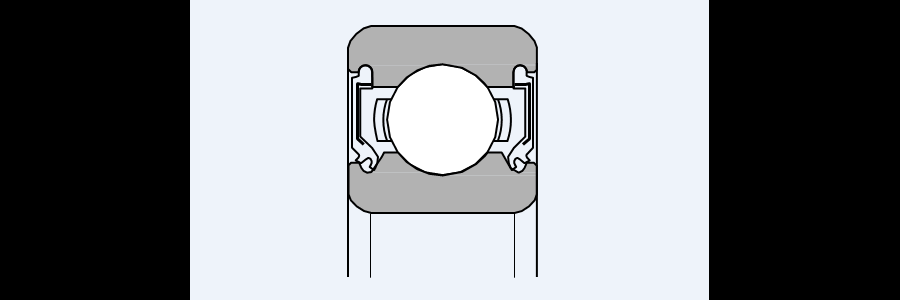
Bearing seals are an extremely important part of bearings, as they protect the bearing against the ingress of dirt, dust, moisture and other foreign objects inside the bearing. At the same time, they also have the task of keeping the lubricant inside the bearing. Both have a significant impact on the service life of the bearing because both the intrusion of dirt and insufficient lubrication inside the bearing lead to premature failure of the bearing. Sheet shields (ZZ), rubber seals (2RS) and non-contact rubber seals are most often used in bearings, depending on the specific requirements and operating environment of the bearing.
| Find bearings in e-shop | Online shop |
Sheet metal bearing shield (2Z or ZZ)
In this case, the shields are made of suitably shaped sheet metal, which is attached to one ring of the bearing. The second ring is not actually touched by the shield and there is a minimal gap at this point. So it's a non-contact shield. Such shields protect the bearing well from dust and effectively retain the bearing grease in the bearing. However, they are not suitable for use where protection against moisture is also required. They are suitable for temperatures from -20° to +120°C
Advantages:
- do not cause additional friction and heating
- effective retention of grease in the bearing (the bearing is lubricated for life)
Disadvantages:
- limited protection capabilities (non-contact shield)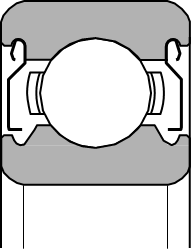
Rubber bearing seals (2RS)
Rubber seals are very often used in bearings as they enable very effective sealing and protection of the bearing against dirt, foreign objects and moisture. In this case, it is a contact seal, which causes increased friction and heating, and consequently reduces the maximum rotations of the bearing. After assembly, the bearing does not require maintenance, as it is lubricated for life with grease, which is retained inside the bearing by the seals. They are typically made of NBR rubber and are suitable for temperatures from -20°C to +100°C.
Advantages:
- excellent sealing against dirt and moisture
- resistance to many aggressive materials
- maintenance-free (the bearing is lubricated for life)
Disadvantages:
- increased friction, heating and consequently lower maximum revolutions
Non-contact rubber bearing seals (2BRS, 2RZ, VV, LLB)
The non-contact rubber seal creates an extremely small gap between the seal and the bearing ring. Instead of sealing by making direct contact with the inner surface of the bearing ring, non-contact seals use an air or oil pad that creates a protective barrier. These seals are very effective in keeping the lubricant inside the bearing. They create minimal additional friction with good protection against dirt.
Advantages:
- good sealing with minimal friction
- maintenance-free (the bearing is lubricated for life)
Disadvantages:
- protection against dirt is worse than in the case of contact sealing
Designation of bearing seals
Different manufacturers designate bearing seals differently, but they are similar in function and shape. For this purpose, we have prepared a comparative table of bearing seal designations according to the individual manufacturer.
|
Seal from both sides of bearing |
||||||||
|
Brand |
FAG |
NACHI |
NKE |
NSK |
NTN |
SKF |
SNR |
ZEN |
|
2x Sheet metal shields |
2Z |
ZZ(E) |
2Z |
ZZ |
ZZ |
2Z |
ZZ |
ZZ |
|
2x Rubber seals |
2RSR / 2HRS |
2NSL / 2NSE(9) |
2RSR / 2RS2 |
DDU |
LLU |
2RS1 / 2RSH |
EE |
2RS |
|
2x Low-friction contact rubber seals |
– |
– |
– |
– |
LLH |
2RSL |
– |
– |
|
2x Non-contact rubber seals |
2BRS |
2NKE(9) |
– |
VV |
LLB |
2RZ |
– |
2DU |
Warning
All serially sealed bearings usually contain a lifetime amount of grease inside the bearing and therefore do not require additional lubrication during their lifetime.
If the bearing is exposed to oil lubrication, it must be open (without seals) so that the oil can enter the bearing without interruption. Otherwise, it may happen that the oil gradually washes the grease out of the sealed bearing, which in turn leads to failure due to inefficient lubrication.
Bearings closed on one side
One-sided sealed bearings are also available on the market, which are used in cases of oil lubrication. In this case, the bearing is protected from the ingress of dirt and moisture on one side and is open on the other side to ensure uninterrupted oil lubrication. In this case, manufacturers use the designations below.
|
Seal from one side of bearing |
||||||||
|
Brand |
FAG |
NACHI |
NKE |
NSK |
NTN |
SKF |
SNR |
ZEN |
|
1x Shield |
Z |
Z(E) |
Z |
Z |
Z |
Z |
Z |
Z |
|
1x Rubber seal |
RSR / HRS |
NSL /NSE(9) |
RSR / RS2 |
DU |
LU |
RS1 / RSH |
E |
RS |
|
1x Low-friction contact rubber seal |
– |
– |
– |
– |
LH |
RSL |
– |
– |
|
1x Non-contact rubber seal |
BRS |
NKE(9) |
– |
V |
LB |
RZ |
– |
DU |
Comparison table of bearing seals
|
Type, code no. |
Shield type |
Rubber seal type |
|||
|
Non-contact type |
Contact type |
Non-contact type |
Low friction contact type |
||
|
Designation by brand |
FAG |
2Z |
2RSR / 2HRS |
2BRS |
– |
|
NACHI |
ZZ(E) |
2NSL / 2NSE(9) |
2NKE(9) |
– |
|
|
NKE |
2Z |
2RSR / 2RS2 |
– |
– |
|
|
NSK |
ZZ |
DDU |
VV |
– |
|
|
NTN |
ZZ |
LLU |
LLB |
LLH |
|
|
SKF |
2Z |
2RS1 / 2RSH |
2RZ |
2RSL |
|
|
SNR |
ZZ |
EE |
– |
– |
|
|
ZEN |
ZZ |
2RS |
2DU |
– |
|
|
Construction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sheet steel fixed to outside ring. Clearance on inner ring. |
Synthetic rubber molded to a steel plate and fixed on outside ring. Seal edge contact on inner ring. |
Synthetic rubber molded to a steel plate and fixed on outside ring. Seal edge is aligned with inner ring with very small clearance. |
Basic construction the same as 2RS type. Specially designed lip on edge of seal. Low fricition construction. |
||
|
Performance comparison |
Friction |
Very Low |
Medium |
Very Low |
Low |
|
Dust protection |
Good |
Best |
Very Good |
Excellent |
|
|
Water protection |
Poor |
Very good |
Poor |
Good |
|
|
High speed capacity |
Same as open type |
Limited by contact seals |
Same as open type |
Better than 2RS-type |
|
|
Temp. range |
-20 ℃~120 ℃ |
-20 ℃~100 ℃ |
-20 ℃~100 ℃ |
-20 ℃~100 ℃ |
|
| Find bearings in e-shop | Online shop |






























Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *